E
- EDC Fine Structure Length Fraction
- in Eqn. (3413).
- EDC Fine Structure Time
- The fine structure (flamelet) region residence time, in Eqn. (3414).
- EDC Mean Reaction Rate Ratio
- The ratio that is calculated by Eqn. (3413) which is used to modify the chemical reaction source term in Eqn. (3412).
- Eddy-Current Loss Coefficient
- Corresponds to the coefficient in Eqn. (4344).
- Eddy Velocity Fluctuation
- The difference between the instantaneous and Reynolds-Averaged velocity in eddies of the particles. It is the quantity in Eqn. (2999).
- EdgeLength
- Displays the average edge length on faces. Only available for surface meshes.
- Effective Conductivity
- The effective
thermal conductivity given by
where
is the turbulent Prandtl number.
For porous regions this field function is given by
- Effective Electrical Conductivity
- in Eqn. (4093), and in Eqn. (4097).
- Effective Intermittency
- The transported variable , see Eqn. (1510).
- Effective Mass Diffusivity of <species>
- The effective mass diffusivity, , where is the molecular diffusivity, is the turbulent viscosity, and is the turbulent Schmidt number. For laminar flows, , and .
- Effective Mass Diffusivity of [component] in [multi-component material]
- For multi-component phases only.
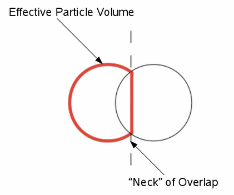
- Effective Particle Volume
- The volume of a particle
minus the overlapping volume beyond the plane(s) of intersection with any
other particle(s).
- Effective Plastic Strain
- Represents a scalar measure for the plastic strain (see Eqn. (4519)).
- Effective Viscosity
- The sum of the laminar and turbulent viscosities .
- Effective Volume
-
Function Name: EffectiveVolumeDimensions: [Volume] Default units: m3 Type: Scalar Activated by: Coupled or Segregated Flow, Porous Media Thermal Equilibrium, Porous Media Thermal Non-Equilibrium - Effective Volume of [phase]
- The effective volume of the Eulerian phase.
- Efficiency Factor
- The efficiency factor models an increase in the turbulent flame speed due to eddies smaller than the thickened flame, which are lost in the artificial thickening process. See in Eqn. (3463).
- Elastic Electron Collisional Cross Section
- Elastic collision momentum transfer cross-section which is used to calculate the collision frequency.
- Electrical Conductivity
- Represents the scalar electrical conductivity of isotropic materials (see Eqn. (4228), Eqn. (4093)) and (see Eqn. (4097)).
- Electrical Conductivity (Imag, Real, Phase, Magnitude)
- Represent the imaginary part, real part, phase, and magnitude of the complex electrical conductivity in Eqn. (4263).
- Electrical Conductivity (Symmetric Tensor)
- For porous regions and anisotropic solid regions, the electrical conductivity in Eqn. (4228) is a symmetric tensor. For porous regions, this field function represents the effective electrical conductivity tensor (see Eqn. (4230)).
- Electric Current Density
- Vector field function that represents the electric current density in Eqn. (4228).
- Electric Current Density (Imag, Real, Phase, Magnitude)
- Represent the imaginary part, real part, phase, and magnitude of the complex electric current density in Eqn. (4269).
- Electric Current Density-Z
- Vector field function that represents the component of the electric current density normal to the 2D domain.
- Electric Current Density-Z (Imag, Real, Phase, Magnitude)
- Represent the imaginary part, real part, phase, and magnitude of the complex electric current density . The electric current density magnitude, , is also referred to as the peak value.
- Electric Current Sheet (Imag, Real, Phase, Magnitude)
- Represent the imaginary part, real part, phase, and magnitude of the complex electric current sheet (see Eqn. (4313)).
- Electric Field
- in Eqn. (4093).
- Electric Flux Density
- Corresponds to the electric flux density in Eqn. (4219).
- Electric Potential
- in Eqn. (4100).
- Electrochemical Equilibrium Potential of [Reaction] of [Surface Mechanism]
- Displays the electrochemical equilibrium potential in Eqn. (4122) and Eqn. (4139).
- Electrochemical Reaction Rate of [Reaction] of [Surface Mechanism]
- Displays the
electrochemical reaction rate (specific reaction current density),
, in:
- Eqn. (4129) when using the Butler Volmer reaction method
- Eqn. (4132) when using the Tafel reaction method
- Eqn. (4134) when using the Tafel Slope (log 10) reaction method
- Eqn. (4136) when using the Transport Limited Tafel Slope (log 10) reaction method
- Electrochemical Species Residence Time
- Displays the residence time of electrochemical species within a specified volume. See Eqn. (4178).
- Electromagnetic Force Density
- Electromagnetic force density at an interface between two materials ( in Eqn. (4349)).
- Electromagnetic Nodal Force
- Represents the electromagnetic force at mesh nodes, as defined in Eqn. (4353).
- Electromagnetic Stress
- Electromagnetic stress vector ( in Eqn. (4351)). The electromagnetic stress vector can be used to calculate the total electromagnetic force acting on a body surrounded by air (see Eqn. (4350)).
- Electromechanical Stress Tensor
- Electromechanical stress tensor , as defined in Eqn. (4347) (for linear materials) and Eqn. (4348) (for nonlinear materials).
- Electron Elastic Collision Energy Source
- Electron elastic collision energy source term, in Eqn. (4193).
- Electron Energy Density
- Electron energy density, .
- Electron Number Density (Ap Coefficient, Correction, Gradient, Limiter, Recon, Residual)
- Electron number density, .
- Electron Ohmic Energy Source
- Electron Ohmic heating energy source term, in Eqn. (4193).
- Electron Temperature
- Electron temperature, .
- Electrostatic Force Density
- Electrostatic force density at the interface between two materials ( in Eqn. (4276)). At the interface between materials with the same permittivity , evaluates to zero.
- Element Type
- Scalar field function that identifies each element topology with a unique number. To visualize the mesh element type, display this field function in a scalar scene. If all the elements in the mesh are of the same type, the color bar will display a single number. The values associated with each element topology are listed in the section, Element Type Reference.
- Energy Residual
- This residual becomes
available in simulations involving heat transfer for fluids alone when the
energy solver has the Temporary Storage
Retained property activated.
In a multiphase continuum, a version of this field function is created for each phase.
- Energy Source
- The rate of energy transfer from the Lagrangian phase to the Eulerian phase through the phase interaction.
- Elliptic Blending Function
- The transported variable .
- Enthalpy of [species]
- The enthalpy of the specified species.
- Enthalpy of [component] in [multi-component material]
- For multi-component phases only.
- Entropy
- Displays the entropy of the fluid.
- Entropy Function
- Measures the degree to which a flow is isentropic. Represented by in [eqnlink].
- Equivalent Plastic Strain
- Represents a scalar measure for the plastic strain that is accumulated as the plastic deformation increases (see Eqn. (4518)).
- Equivalence Ratio
- in Eqn. (3576).
- Erosion Rate
- The sum of Abrasive Wear Rate and Impact Wear Rate. It is the quantity in Eqn. (3306).
- Error Estimate of <variable>
- Highlights where high numerical inaccuracy impact the accuracy of the respective cost function.
- Evaporation Rate of <Vapor Component> of <Phase>
The rate of change of each transferred component due to quasi-steady evaporation.
Only active when Temporary Storage Retained is activated within the Segregated MMP solver.- Exhaust Gas Recirculation Mass Fraction
- in Eqn. (3875), Eqn. (3876), and Eqn. (3877).
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation Mole Fraction
- Mass fraction of product (burnt) species in Eqn. (3452).
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation Mole Fraction
- in Eqn. (3946).
- Explicit relaxation factor
- A scaling factor that is used to relax all coupled flow corrections explicitly before they are applied to the flow solution, also known as a damped update.
- Exponential Time Filtered Stress Tensor
- The mean Reynolds-stresses as calculated by the EWA method.
- Exponential Time Filtered Velocity
- The mean velocity as calculated by the EWA method.
- External Ambient Temperature
- The boundary ambient temperature that you specify for convection thermal boundary conditions. This field function is only available on boundaries for which the Convection option has been selected as the Thermal Specification.
- External Heat Transfer Coefficient
- description
- Extra Stress n
- The terms Extra Stress 1, Extra Stress 2, ... that sum to in Eqn. (706). There is a term for each viscoelastic mode used. (Viscoelastic)