O
- Orientation Tensor
- Tensor in Eqn. (749) describing the mean orientation of the short fibers suspended in a viscous flow. (Short Fiber Orientation).
- Overset Cell Status
- Used internally
as a flag in the solvers to identify the status of each cell during the
solution process of the equations. This function provides more information
about the result of the Overset Assembly process. The available values
are:
- 1 – inactive
- 0 – active
- -2 – acceptor
- -1 – acceptor that used to be a donor
- Overset Cell Type
- Used by the
Overset Assembly process to identify the status of each cell. It gives more
information about the cells with regard to the Overset Assembly process. Can
be used to analyze errors. The available values are:
- 0 – active
- -1 – inactive cell that resides outside of the background mesh
- -2 – inactive cell that is covered by another overset region. Consequently, this type can only occur for multiple overset meshes.
- -3 – inactive cell inside a zero gap zone
- 1 – donor
- 2 – active, intermediate cell layer used by the hole cutting process.
- 3 – acceptor
- Overset Error Status
- Indicates the
status of each cell that has an error. The available values are:
- 0 – cell has no error
- 5 – cell is an acceptor cell that has inactive donor cells
- 6 – cell is an acceptor cell that has zero donor cells
- 20 – cell is a donor cell, but is inactive
- 30 – an inactive face: that is, a face between an active cell and an inactive cell
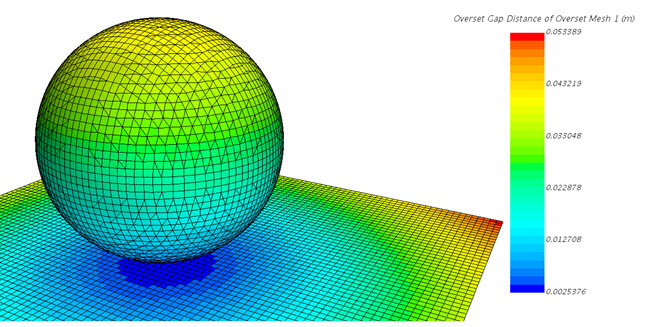
- Overset Gap Distance Field Function
- Provides the gap
distance between wall-type boundaries of connected overset regions, or an
overset region with a background region for the purposes of determining the
cell-density required on the boundary surfaces to resolve the flow in small
gaps (using prism layers).
The gap distance is calculated from the boundary to each cell face-centroid on the boundaries of the connected regions. It helps determining suitable user-inputs for the near-wall morphing / cell shrinkage feature.
The Overset Gap Distance Field Function is only available when you create overset mesh interfaces. See Setting up Overset Regions. Boundary types considered as walls are: wall, contact, baffle, and porous-baffle.
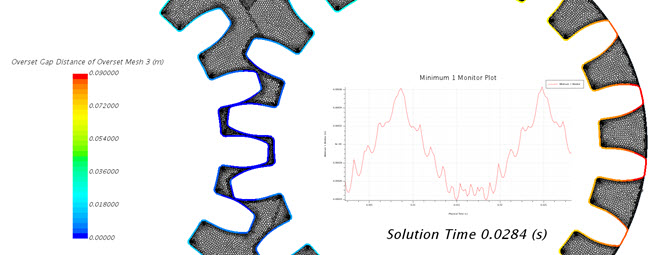
In some cases, it is prudent to report and monitor the minimum gap between two surfaces as they move together (or apart) over time—for example, a valve plug closing against its seat, or teeth on a gear-wheel engaging with its counterpart.
- Overset Grid Area
- Estimates the
area of all regions in the simulation. For overset mesh simulations, this
area estimation is more accurate than the area computation of the Area field
function, because it avoids double-summation of the area of overlapping
cells in overlapping regions.
The Overset Surface Integral report uses this field function for a more accurate integration compared to the standard Surface Integral report. See Overset Surface Integral Report.
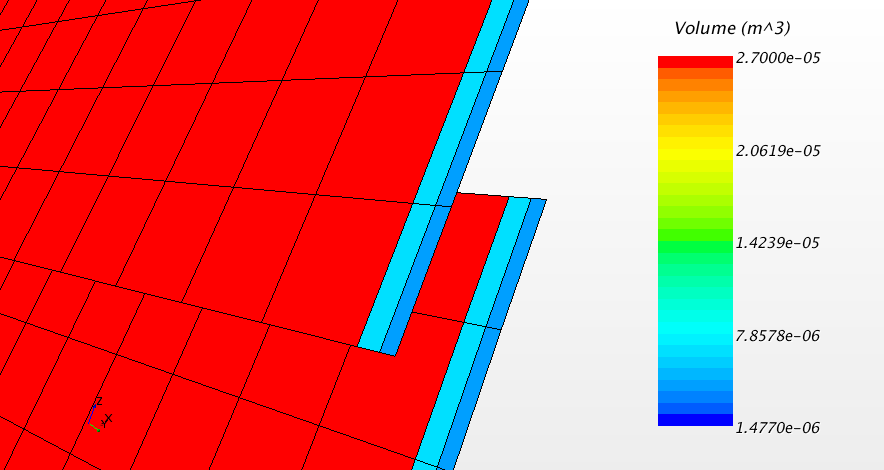
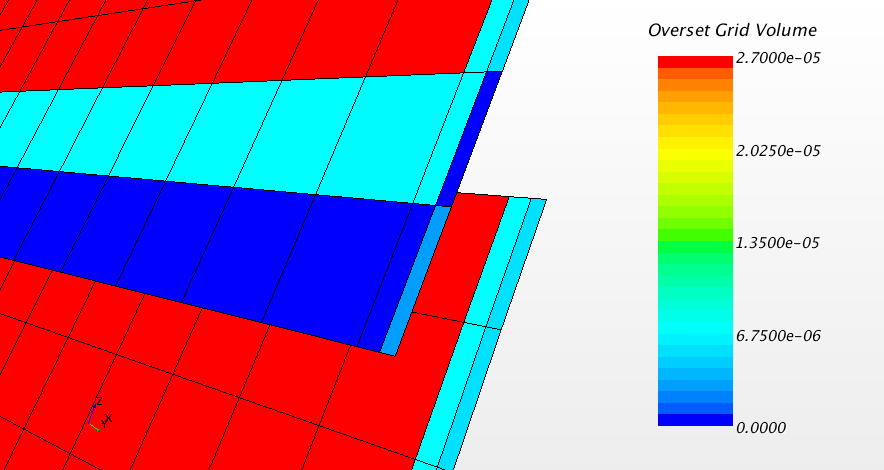
- Overset Grid Volume
- Estimates the
volume of all regions in the simulation. For overset mesh simulations, this
volume estimation is more accurate than the volume computation of the
Volume field function, because it avoids
double-summation of the volume of overlapping cells in overlapping regions.
The Overset Volume Integral report uses this field function for a more accurate integration compared to the standard Volume Integral report for overset simulations. See Overset Volume Integral Report.
When you use this field function, either through an Overset Volume Integral or for visualization in a scalar scene, the simulation runtime can increase significantly. To speed up the simulation time, do not evaluate the field function at every time step, but select and increase Frequency. You can similarly increase the time-step frequency for a scene by selecting .
- Overset Interpolation Cell Size Ratio
- Reports the
ratio of cell lengths between the background region and the overset
region(s). After an overset intersection, a cell size ratio is computed for
each acceptor cell defined by
See also Donor Search and Overset Cell Type regarding the definitions of acceptor and donor cells.
The possible values of Dimension =- 2 – 2D mesh
- 3 – 3D mesh
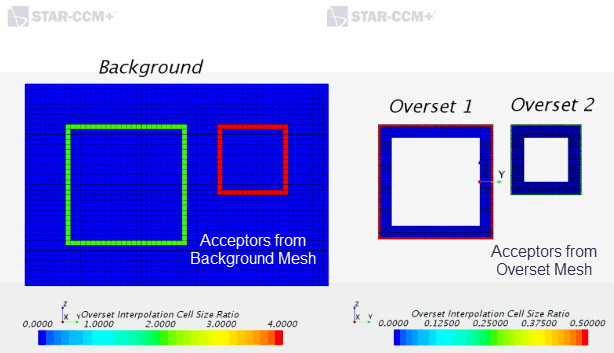
The mesh sizes are as following:- Overset 1 Base Size: 0.05m
- Overset 2 Base Size: 0.025m
- Background Base Size: 0.1m
- Overset Interpolation Type
- Indicates which
interpolation type Simcenter STAR-CCM+ is
using for the interpolation between background mesh and overset mesh.
Although you specify the interpolation type (see Option), Simcenter STAR-CCM+ can switch to a more robust interpolation scheme in
the course of the simulation when the current mesh configuration makes it
impossible to apply the selected interpolation scheme. For example, when you
select a Linear or a
LinearQuasi2D
interpolation scheme, Simcenter STAR-CCM+
can revert to the more robust Distance
weighted scheme if the conditions for the
selected interpolation scheme cannot be met.
The possible values are:
- 0 – Distance Weighted
- 1 – Linear
- -1 – No overset interface present
- -2 – Not an acceptor cell, that is, no interpolation takes place from donor to acceptor
- 4, 5, or 6 – Inverse Distance type interpolation. Indicates that the interpolation is difficult and less accurate. When you see these values, you are advised to improve the mesh, for example, by refining the overlap area or by ensuring similar cell sizes for background and overset mesh in the overlap area.
- Overset Transition
- description