Transforming a Body
In 3D-CAD, you can perform transformations on both BRep and facet bodies. Typical transformations include translations, rotations, reflections, scaling, and coordinate system transforms.
- In the Bodies manager node, right-click the desired body and select . To select multiple bodies, hold down the <Ctrl> key.
- Define the properties for the transformation. See the relevant sections:
- Expose any properties as design parameters by clicking the (Expose Parameter) button.
- Choose whether to apply the transformation to the original body, or to a copy of the original. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation.
- Click OK.
The transformation is applied to the selected bodies. Each operation creates a feature node in the 3D-CAD feature tree.
Translating a Body
| Direction Type | Specifies how you define the translation of the body.
|
| Coordinate System Source | Defines the coordinate system for the transformation. If you have specified an alternative coordinate system within the simulation, you can define the transformation with reference to this coordinate system instead of the default, Laboratory. |
| Translation Vector (X, Y, Z)/(R, θ, Z)/(R, θ, φ) (Only available if Direction Type is set to Specified) | Defines the direction of translation. Enter the components of the translation vector or use the triad within the 3D-CAD View window. |
| Distance (Only available if Direction Type is set to Reference Axis) | Specifies the distance the reference axis is moved. |
| Action | Specifies whether to carry out the transformation on the original body or a copy of the original body. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation. |
Scaling a Body
Scaling a body proportionally increases or decreases its size with respect to the selected coordinate system.
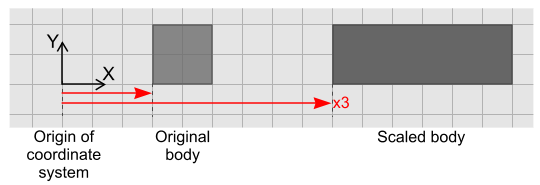
The origin of the coordinate system may not always be the same as the origin of the sketch plane. If you are using a coordinate system other than the default, you can check the coordinates of the origin by selecting the relevant node under in the main simulation tree. The origin is displayed in the Properties window.
| Bodies to Scale | Specifies the bodies used in the operation. |
| Scale all dimensions uniformly | Specifies whether the selected bodies are scaled uniformly in all directions. If you want to scale the body uniformly in all directions, activate this option. The value that you enter in the first Scale Factor text box applies to the remaining text boxes (which are grayed out) |
| Scale Factor | Defines the amount by which the bodies are scaled. Enter the scale factor for each direction: X, Y, Z, and R (cylindrical coordinate system only). Alternatively, in the 3D-CAD View scene, you can click and drag the axes of the triad. |
| Coordinate System Source | Defines the coordinate system for the transformation. If you have specified an alternative coordinate system within the simulation, you can define the transformation with reference to this coordinate system instead of the default, Laboratory. |
| Action | Specifies whether to carry out the transformation on the original body or a copy of the original body. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation. |
Rotating a Body
Rotating a body turns it around a specified axis.
| Rotate Axis—defines the axis about which the selected bodies rotate. If you define the direction or position using a design parameter the arrow or triad is hidden in the scene. | |
| Bodies to Rotate | Specifies the bodies used in the operation. |
| Axis Type | Specifies the method you use to define the rotation of the body.
|
| Coordinate System Source | Defines the coordinate system for the transformation. If you have specified an alternative coordinate system within the simulation, you can define the transformation with reference to this coordinate system instead of the default, Laboratory. |
| Axis Direction (X, Y, Z)/(R, θ, Z)/(R, θ, φ) | Defines the direction vector of the axis of rotation. Enter the components for direction vector. Alternatively, in the 3D-CAD View scene, click and drag the light blue arrow to change the orientation of the rotation. |
| Axis Position (X, Y, Z)/(R, θ, Z)/(R, θ, φ) | Defines the origin of the axis of rotation. Enter the coordinates of a point that lies on the axis of rotation or reposition the triad within the 3D-CAD View window. |
| Angle | Specifies the angle of rotation. You can specify the angle as a constant value, design parameter, or using the arrow in the 3D-CAD View scene. If the angle is set using a design parameter the arrow is hidden in the scene. |
| Action | Specifies whether to carry out the transformation on the original body or a copy of the original body. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation. |
Mirroring a Body
| Mirror Plane —defines the plane about which the selected bodies are mirrored. If you define the normal or position using a design parameter the arrow or triad is hidden in the scene. | |
| Coordinate System Source | Defines the coordinate system for the transformation. If you have specified an alternative coordinate system within the simulation, you can define the transformation with reference to this coordinate system instead of the default, Laboratory. |
| Normal (X, Y, Z)/(R, θ, Z)/(R, θ, φ) | Defines the direction vector that is normal to the mirror plane. You can enter the components of this direction vector or click and drag the light blue arrow to change the orientation of the mirroring, in the 3D-CAD View scene. If you define the normal using a cylindrical or spherical coordinate system you can only define normal coordinates by entering the direction vector. |
| Position (X, Y, Z)/(R, θ, Z)/(R, θ, φ) | Defines a point that lies on the mirror plane. Enter the coordinates of this point or reposition the widget within the 3D-CAD View window. |
| Action | Specifies whether to carry out the transformation on the original body or a copy of the original body. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation. |
Transforming a Body Using Coordinate Systems
| Bodies to Transform | Specifies the bodies to transform in the operation. Select bodies from the 3D-CAD View scene or from the Bodies node in the feature tree. |
| From | Specifies the source coordinate system. Set Coordinate System Source to the coordinate system that you want to transform from. The default option is the imported coordinate system. If you choose a reference coordinate system, select this from the 3D-CAD View scene or from the 3D-CAD feature tree. |
| To | Specifies the target coordinate system. Set Coordinate System Source to the coordinate system that you want to transform to. The default option is the imported coordinate system. If you choose a reference coordinate system, select this from the 3D-CAD View scene or from the 3D-CAD feature tree. |
| Action | Specifies whether to carry out the transformation on the original body or a copy of the original body. See Creating a Copy During the Transform Operation. |