Defining Boundary Conditions for Conjugate Heat Transfer
Define the boundary conditions for CHT analysis. For the fluid structure interface, you specify the coupling specification between the fluid and the manifold. For the fluid, you define the mass flow rate at the inlets and the temperature of the gas at the inlets and outlet. For the external surfaces of the solid, you use a convection boundary condition. For the manifold plate that in reality is mounted on the engine, you specify a fixed temperature.
To define the fluid structure coupling of the interface:
- Select the , and set Option to Uncoupled.
To set the mass flow rate and the temperature of the gas at the inlets:
-
Edit the
node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting 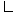
Value 0.1 kg/s 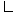
Value 1200 K
Set the temperature at the outlet to
match the temperature at the inlets. This setting is relevant only if reversed flow
occurs at the outlet:
- Select the node and set Static Temperature to 1200 K.
- Expand the node.
-
Edit the
External node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting Physics Conditions 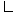 Thermal Specification
Thermal Specification
Condition Convection Physics Values 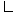
Value 420 K 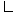
Value 600 W/m^2-K
For the cylinder head, you specify a constant temperature of 440 K. This assumption is realistic, as the temperature of the cylinder head is typically kept under control using a water jacket.
-
Edit the
ToCylinderHead node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting Physics Conditions 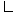 Thermal Specification
Thermal Specification
Condition Temperature Physics Values 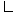
Value 440 K The remaining boundaries are set to Adiabatic.
- Save the simulation.