Running the Simulation
As you are seeking the steady-state solution in the fluid and the solid, it is both convenient and valid to initially solve for the fluid flow, then for conjugate heat transfer, and finally solve for the solid displacement while holding the thermal field fixed.
-
Edit the
node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting Displacement Criterion Enabled Deactivated Force Criterion Enabled Deactivated Maximum Steps Maximum Steps 100 - Expand the Solvers node.
- Multi-select the Finite Element Solid Energy and Solid Stress Solver nodes and activate Solver Frozen.
-
Click
 (Run).
(Run).
To solve for the solid
temperature, you reactivate the Finite Element Solid Energy
and run the simulation. The Finite Element Solid Energy
solver allows you to choose between a direct and an iterative solution method. For
larger cases, the iterative method speeds up convergence:
-
Select the Finite Element Solid Energy node and set the
following properties:
Property Setting Under-Relaxation Factor 0.999 Solver Method Iterative Solver Frozen Deactivated - Select the node and set Maximum Steps to 200.
-
Click
 (Run).
(Run).
-
Open the
.
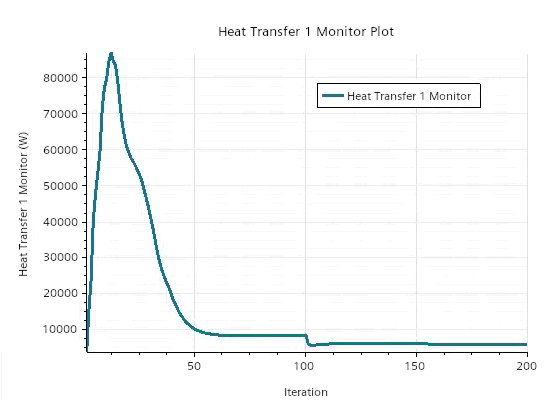
The heat transfer plot shows that the solution has converged:
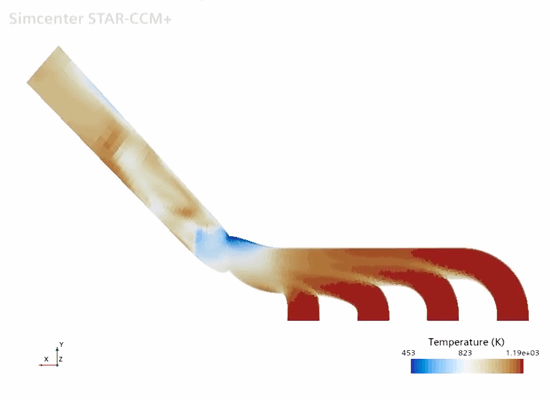
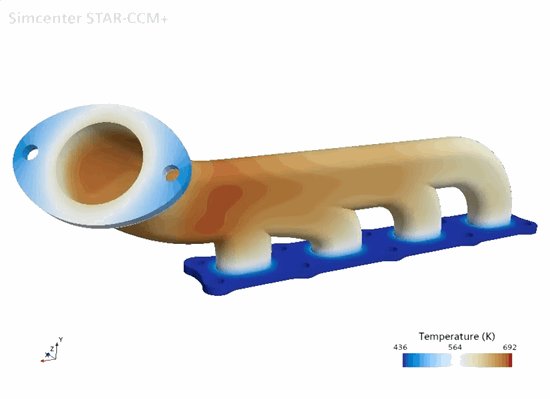
To visualize the temperature distribution throughout the gas and the manifold:
-
Open the scenes,
Fluid Temperature and
Manifold Temperature.
To solve for the fluid displacement,
run the solid stress solver for two iterations:
- Select the node and set Maximum Steps to 202.
- Select the Solid Stress Solver node and deactivate Solver Frozen.
-
Click
 (Run).
(Run).
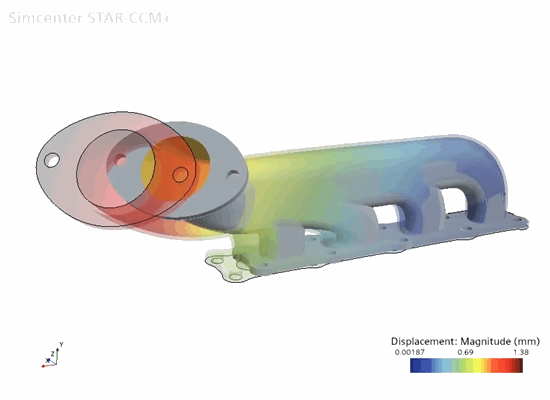
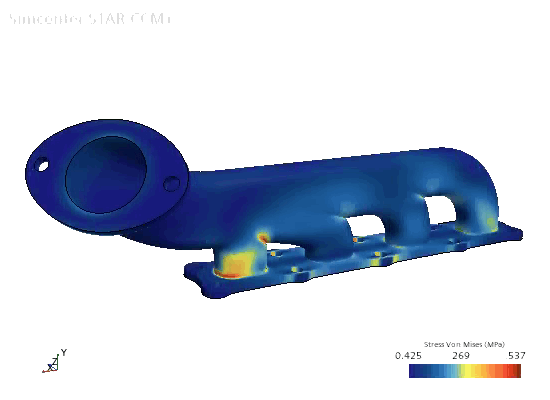
To visualize the thermal expansion and stress on the solid:
-
Open the scenes,
Displacement and
von Mises Stress.
- Save the simulation.