Analyzing the Effects of Volumetric Heat Exchange
After the simulation is complete, you visualize the results. You compare these with the results from the first part of the tutorial, where you exclusively used Surface Photon Monte Carlo to model radiative heat transfer, to assess the effects that absorption has on the solution.
-
To examine the total irradiation on the rear housing, open the Irradiation Rear Housing Plot.
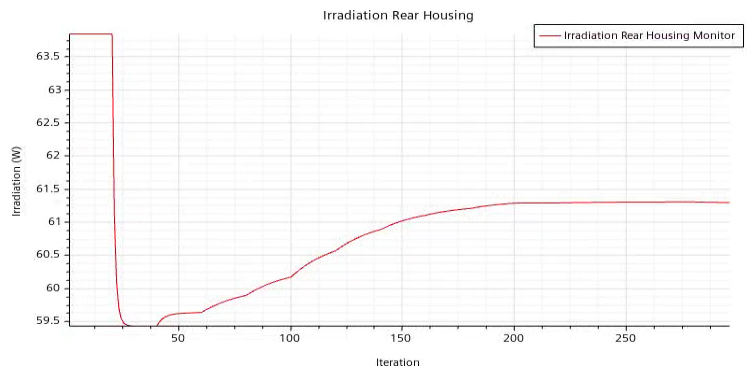
Irradiation of the rear housing is reduced due to the absorption of solar and thermal radiation by the lens and halogen bulb. The lens and bulb both have low absorptivity, so this reduction is small but is still noticeable.
-
To examine the direct solar irradiation distribution, open the Direct Solar Irradiation scene.
The following screenshot shows the direct solar irradiation on the reflector of the headlamp:
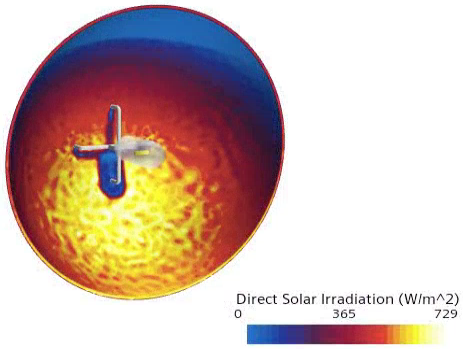
Direct solar irradiation is slightly reduced due to absorption of incident solar radiation by the lens.
-
Click through the Reflector Temperature and
Lens Temperature scenes.
The following screenshots show the temperature distributions on the reflector and the lens of the headlamp.
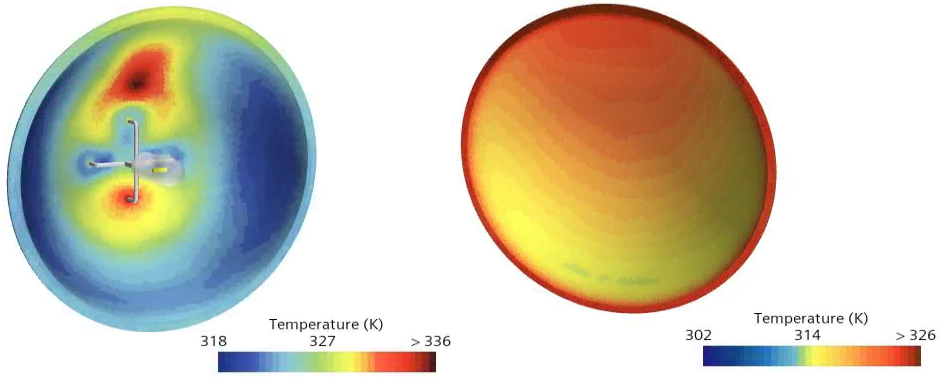
The temperature is higher all over the reflector of the headlamp. This is most noticeable in and around the hotspot, and around the edges of the reflector. As an effect of absorption, the transparent components—the lens and the halogen bulb—have higher temperatures. More heat is transferred from the surfaces of these components, both by convection and by conduction, resulting in a larger and hotter hotspot and in an increase in temperature around the edges of the reflector that are in contact with the lens.