Study Types
Design Manager offers several types of design study by which you can explore the design space of your product.
While CAD robustness studies and performance assessment studies do not require specific licensing, design optimization studies are only available with Simcenter STAR-CCM+ Intelligent Design Exploration licensing.
 CAD Robustness
CAD Robustness
A CAD Robustness study allows you to check whether the CAD geometries that are created from geometric input parameters are valid. Invalid geometries can cause meshing problems in the upcoming studies. Before running a performance assessment or an optimization study, you can run a CAD robustness study to check the geometric validity of designs in your design space.
You supply the input parameter values using one of the following sampling methods:
- Manual
- Sweep
- Latin Hypercube
For details on how you define the input parameter values, see Manual, Sweep, or Latin Hypercube Sampling DOE study.
A CAD Robustness study changes the parameter values and updates the CAD geometry—it does not push the modified geometry through the mesh pipeline and run a simulation. If a change to an input parameter causes the CAD geometry to become invalid, Design Manager sets the status of the design to failed.
Usually, you perform a CAD Robustness study before you run a performance assessment or optimization study in order to check if the CAD geometry successfully updates over the given range of parameters. In case of high failure rates of the CAD robustness study, adjust the parameters range accordingly, try to simplify the geometry, or to re-parametrize the geometry.
Performance Assessment
 Manual
Manual - In a Manual study, you define a set of designs using tabulated data, where each design is a certain combination of input parameter values. You provide the set of designs before starting the analysis.
 Sweep
Sweep - In Sweep mode, before starting the analysis, you provide values for the input parameters. For each input parameter, you can either provide a constant value or a list of discrete values. You can also define a lower and an upper bound for a parameter in conjunction with a specified increment or resolution. Design Manager then creates a full factorial design sweep that goes through all combinations of parameter values.
 Smart Sweep
Smart Sweep - A Smart Sweep study is an advanced sweep study where you create design runs along specified operating conditions. At each sweep, the step between two designs is controlled through a stepping parameter, which is one of the input parameters of the smart sweep study. The end of each individual sweep is determined through stopping criteria.
One example application for the smart sweep is in generating the performance map for compressors. The smart sweep intelligently finds the bounds of the performance map based on the criteria supplied.
You supply the initial values for input parameters at the start of each sweep. You define several values/combinations of input parameter(s) through the Design Study - Design Table. A smart sweep stops when all the defined sweeps have run. For more details, refer to: 设置智能扫掠研究.
Design Optimization (Simcenter STAR-CCM+ Intelligent Design Exploration)
 Optimization
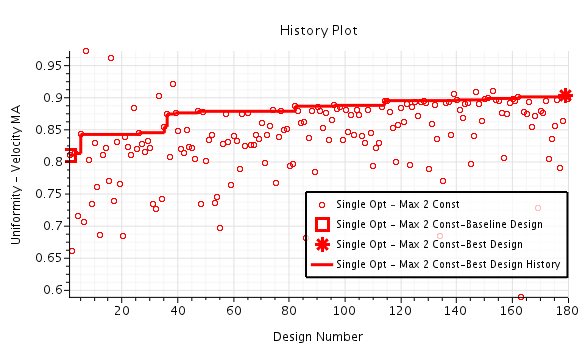
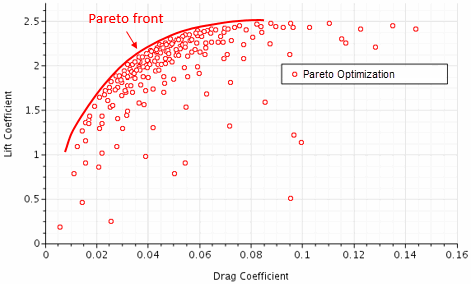
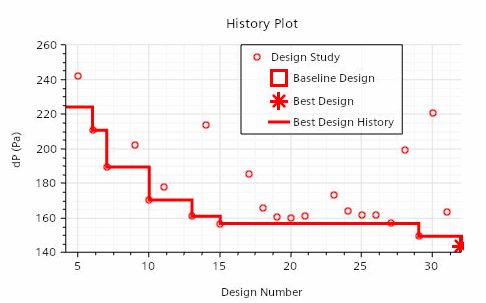
Optimization - In an Optimization study, you define one or more objectives that the analysis must meet as best it can. Along with the objectives, you define input parameters in the same manner as for a Sweep study. During the analysis, a search algorithm chooses the parameter values for the designs so as to best meet the analysis objectives.
 DOE
DOE - A DOE (Design Of Experiments) study
is used to examine how sensitive input parameters affect a given design,
either locally around the best design or in a larger area of the design
space.
In a DOE study, the two settings DOE Type and Parameter Type specify the final input parameter values. The DOE Type determines the sampling method—How design points are selected from the design space.
The available DOE Type options are shown below:
- 2 Level Full Factorial
- 3 Level Full Factorial
- Latin Hypercube Sampling
For more details, see DOE Type Reference and DOE 研究的采样方法.
 Adaptive Sampling
Adaptive Sampling- An Adaptive Sampling
study intelligently characterizes the design space guided by your goals
for the study. Adaptive sampling uses the Adaptive Strategy you select
to give the best possible sampling for the number of evaluations you
specify. The result is an efficiently-constructed set of designs that
you can use to create surrogates and train other kinds of metamodels.
This iterative algorithm is an efficient method for finding design
points within the number of Designs to
Run.
An Adaptive Sampling study allows you to specify design seeds which are used for the initial sampling. See also 使用预定义设计设定研究种子 and Adaptive Sampling Reference.
If you do not provide design seeds, the adaptive sampling study uses an Optimal Latin Hypercube method to generate initial sample points.
Compared to a DOE study, the adaptive sampling strategy is faster at finding a precise description of the design space of interest. In the case of surrogate generation, the adaptive sampling algorithm specifies the best fit surrogate properties automatically. You can apply the Adaptive Sampling study type to:
- Create a surrogate with a precise global description of the design space.
- Create a surrogate with a precise local description of a specific area, for example, where a response is the largest.
- Find more designs in a specific area, for example, where a sharp change occurs in a response.
 Robustness and Reliability
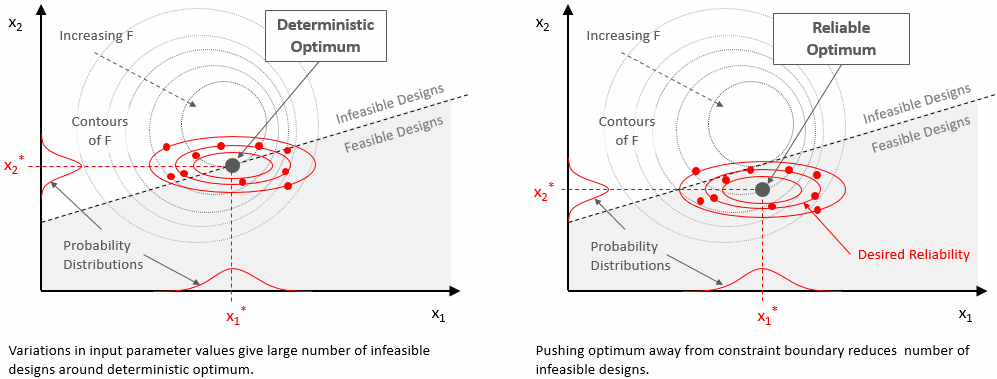
Robustness and Reliability- A Robustness and Reliability study helps you assess the robustness and reliability of a design, that is, how minor variations in the input parameter values affect the outputs.
| 注 | When increasing Designs to Run for a Robustness and Reliability study without Clear Study, the extended design number appends to the previously executed designs. For example, you increase the Designs to Run from 100 to 200, the second design run starts with the number 101 ends with the number 300. To avoid this, you are advised to use the right-click action Clear Study when changing the Designs to Run property. |
- An Optimization study evaluates designs over a broad range of input parameters and parameter values. This study gives you the best design.
- A DOE study evaluates the input parameters in a small range of parameter values about the best design. This approach gives you the parameters that have the greatest impact on the performance of the design.
- A Robustness and Reliability study uses the sensitive parameters identified in the DOE study to determine the robustness of the best design.