Generating the Surrogate Models
To run the robustness and reliability study later on with 500 designs efficiently, surrogate models, also known as response surface models (RSM), are required for the moving-averaged (MA) pressure drop and uniformity. You generate these surrogates using an Adaptive Sampling study based on the best design.
To obtain a surrogate model of high accuracy in the design space around the best design, you specify input parameter permutations in an Adaptive Sampling study. In this study, you use the Balance Local and Global Accuracy adaptive strategy which creates surrogates with good overall fit across the entire design space and also increases the sampling in local regions of interest.
In this tutorial, you pre-select both possible surrogate types— Radial Basis Functions and Kriging. After the study run, the Adaptive Sampling study automatically generates each surrogate with the best fit surrogate type.
In the Kriging surrogate type, you set the Precise Kriging tuning option before you start the Adaptive Sampling study. This option varies shape factors for each variable and provides acceptable tuning results despite higher computational cost.
To generate the surrogate models:- To create a copy of the original study, drag and drop the node onto the Design Studies node.
- Rename the Design Study copy node as Surrogates Generation.
- Select the Surrogates Generation node and set Study Type to Adaptive Sampling.
-
Edit the node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting Adaptive Sampling Settings Designs to Run 90 Adaptive Strategy Balance Local and Global Accuracy Responses to Consider Pressure Drop MA
Velocity Uniformity MA
Surrogates are generated automatically for these two responses.
Surrogate Types Radial Basis Functions
Kriging
 Kriging
KrigingTuning Precise Kriging 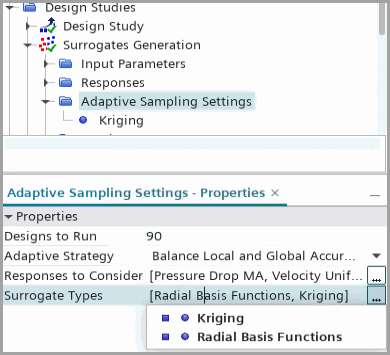
- Right-click the node and select Edit.
-
In the Surrogates Generation - Input
Parameters dialog, specify the following input parameter
ranges:
Name Range Bottom Angle Path [81.0, 87.0] deg Deflector Angle [93.6, 100.4] deg Deflector Horizontal Distance [0.01, 0.21] m Deflector Radius [0.2, 0.4] m Deflector Translation_X [-0.2, 0.0] m Deflector Translation_Y [-0.2, 0.0] m Deflector Vertical Distance [3.0, 3.4 ] m - Click Close.
-
Select the node and set Simultaneous
Jobs to 10.
If you have multiple cores available on your machine, set Compute Processes to a higher number, for example, 6.
-
Select the Surrogates node and make sure that
Auto Compute is activated.
Design Manager computes the surrogates at the end of the Adaptive Sampling study run.
- Select . In the Save dialog, set File name to industrialExhaust_surrogateStudy.dmprj and click Save.
-
Right-click the Surrogates Generation node and select
Run Study.
Design Manager now performs the Adaptive Sampling study and computes the surrogate models at the end of the study run. This part of the analysis may take some time as Design Manager must run 90 simulations.
After the design study run, two generated surrogates with the names Pressure Drop MA_Kriging and Velocity Uniformity MA_Kriging appear under the Surrogates node. The Adaptive Sampling study selects the surrogate type Kriging for both surrogates.