Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Model Reference
The Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) model makes accessible the physics models and setting to define properties and disrcetization for SPH multiphase simulations.
| Theory | 多相流的平滑颗粒流体动力学 (SPH) 法. | ||
| Provided By | |||
| Example Node Path | |||
| Requires |
Pre-requisite
selections:
|
||
| Properties | None. | ||
| Activates | Physics Models |
Automatically selected models: Multiphase Interaction (activated by selecting the Multiphase model) Incompressible Flow (ISPH) Solution Interpolation Adaptive Time-Step |
|
| Region Settings | Physics Conditions:
See Region Settings. |
||
| Field Functions | None. | ||
Region Settings
The following setting applies to each surface region.
- Initial Condition Option
- Lets you customize initial conditions for an individual region.
- Motion Specification Option
-
Method Corresponding Physics Value Nodes - Direct Rotating Motion Values
-
Allow you to define rotating motions directly within the region. It allows you to add rotations independently to different parts of a region.
- Direct Rotating Motion
- This option allows for part subgrouping, that is,
it allows you to define the rotation values
independently for each geometry part of the same
region.
- Direct Rotating Motion Values
- Specifies the properties for the rotation.
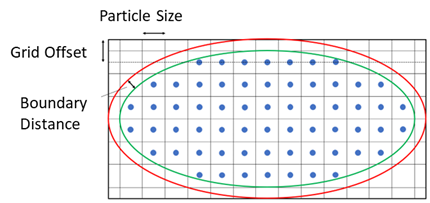
- Particle Base Size
- Specifies the particle size (disretization length) for spacing the fluid particles in the domain. This value represents the target size for the Cartesian lattice used in particle generation.
- Particle Generation
-
Generates particles within the geometry part that represents the initial shape and position of the liquid. The total number of particles is computed by the solver based on the initial liquid volume and particle base size. The particles are distributed uniformly and provide the discretization of the liquid.
- Part Orientation
-
Provides the option to reverse the direction of the surface normal vectors in relation to the fluid location. By default, the surface normals are oriented inward for closed geometry parts, that is, the positive side of a boundary is facing outwards. SHP particles interact with a boundary only on the positive side. Therefore, for external flow around a closed geometry part, the default orientation is correct. However, for internal flow within the geometry part, the default orientation is incorrect and must be reversed.