Setting Material Properties
Since the composition of different types of coal varies, it is important to define the correct composition of the type of coal that is used in the combustor.
The raw coal devolatilizes into char in the particle phase and CoalVolatile in the gas phase. The composition of the coal volatile species is not fixed, but depends on the properties of the coal type being simulated. The proximate and ultimate analysis of the coal sample determines the coal volatile composition. In addition to the proximate and ultimate analysis, the calorific value of the coal type is needed to estimate the heat of formation of the coal volatile.
| Component | Mass Fraction (-) |
|---|---|
| Volatile Matter | 0.5502 |
| Fixed Carbon | 0.3668 |
| Ash | 0.083 |
| H2O | 0.0 |
| Component | Mass Fraction(%) |
|---|---|
| C | 80.36 |
| H | 5.08 |
| N | 1.45 |
| S | 0.94 |
| O | 12.17 |
The proximate analysis gives us a yield of 0.6, the low calorific value of coal is and the specific heat of coal is .
- For the Coal Combustion continuum, select the node and set Method to Mass Weighted Mixture.
- Expand the node.
- Multi-select all of the nodes and set Method to Elemental Composition.
-
Define the composition of the CoalVolatile.
-
Expand the
node and set properties:
Node Property Value Specific Heat Method Constant 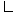 Constant
Constant
1100.0 J/kg-K Heat of Formation 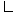 Constant
Constant
-4725729.0 J/kg -
Expand the
node and set the following properties:
Node Property Setting Absorption Coefficient Method Weighted Sum of Gray Gases 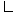 Weighted Sum of Gray Gases
Weighted Sum of Gray Gases
Optical Path Length 1.8 m -
Define the surface materials and specify radiation properties:
- Save the simulation.