Monitoring and Plotting Carbon
You compare the mass of carbon entering the computational domain with the mass of carbon leaving it. When the two mass flow rates reach the same value, you can assume that the solution has converged.
The mass flow rate of carbon at the inlet boundaries is calculated as a product of mass flow rate of coal at the injector, the mass fraction of carbon in the ultimate analysis, and the mass fraction of raw coal at the injector.
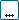
By considering all species in the reaction mechanism that contain carbon, the mass outflow rate of carbon can be defined as:
where is the total mass flow rate, is the molecular weight, is the atomic weight, and is the mass fraction of species .
From the ingoing and outgoing carbon mass flow rates, you create a monitor for a normalized carbon balance that you use later on to define a monitor-based stopping criterion.
To monitor and plot carbon:
-
Create a report for the mass flow rate of incoming carbon.
-
Create a report for the mass flow rate of carbon leaving the computational
domain.
-
Create a plot to display the ingoing and outgoing mass flow rate of carbon:
- Multi-select the Carbon In and the Carbon Out report nodes, right-click one of the selected nodes and select Create Monitor and Plot from Report.
- In the Create Plot From Reports dialog, click Single Plot.
- Rename the node Carbon Balance.
-
Create a report and monitor to calculate the normalized carbon balance.
- Right-click the Reports node and select .
- Rename the Expression 1 node as Normalized Carbon Balance.
- Select the Normalized Carbon Balance node and Definition to (${Carbon In}-${Carbon Out})/${Carbon In}.
- Right-click the Normalized Carbon Balance node and select Create Monitor from Report.
-
Create one more report to analyze the char burnout of the coal particles.
- Right-click the Reports node and select .
- Rename the Char Burn Out 1 node as Char Burnout.
- Select the Char Burnout node and set Parts to Coal.
-
Within the Monitors node, multi-select the following
nodes and set Normalization
Option to Off.
- CO
- CO2
- CoalVolatile
- Continuity
- Energy
- H2
- H2O
- N2
- O2
- Tdr
- Tke
- SO2
- X-momentum
- Y-momentum
- Z-momentum
- Save the simulation.
 (
(