本验证案例利用OpenFOAM计算T型管中流量分配问题,并对计算结果进行验证。
验证文献:R.E. Hayes, K. Nandkumar, H. Nasr-El-Din, “Steady Laminar Flow in a 90 Degree Planar Branch”. Computers and Fluids, Vol 17, pp. 537-553, 1989.
”
1 模型描述
如下图所示的T型管道,几何尺寸L=3.0m, W=1.0m。
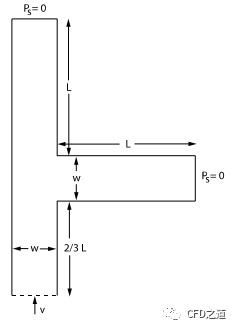
管内流动介质为空气Air,其密度为1 kg/m3,动力粘度0.003333 kg/m-s。空气从下方入口流入,其轴线速度满足雷诺数:
T型管的两个出口静压Ps均为0。
本算例使用simpleFoam求解器进行计算。也可以使用其他任何流动求解器(如icoFoam、pisoFoam、pimpleFoam等)进行计算。
2 OpenFOAM设置
2.1 准备文件
采用simpleFoam算例中的pitzDaily作为模板算例。采用以下命令准备文件。
cp -r /opt/openfoam8/tutorials/incompressible/simpleFoam/pitzDaily .
mv ptzDaily VM10
cd VM10
本算例为层流流动,删除多余的文件,最终文件夹组织结构如下图所示。
2.2 计算网格
本算例网格利用ICEM CFD进行生成。将网格文件VM10.msh放到算例文件夹中。
利用命令转换并检查网格:
fluentMeshToFoam VM10.msh
checkMesh
确保计算网格检查结果没有错误信息。如下图所示。
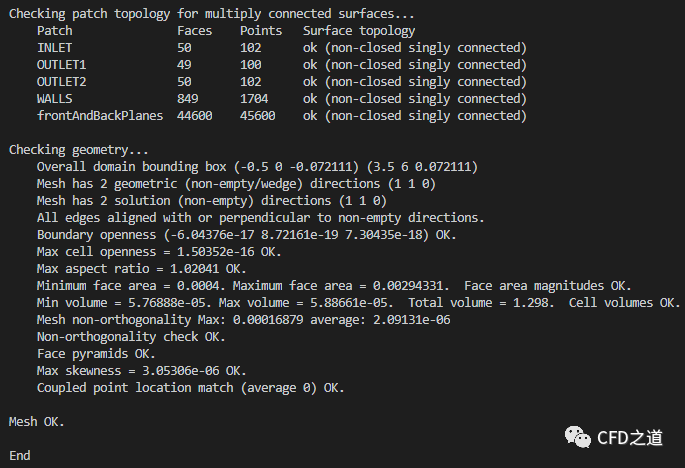
本算例的boundary文件内容不需要修改。
2.3 设置介质属性与物理模型
1、momentumTransport文件
设置使用层流计算,文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object momentumTransport;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
simulationType laminar;
2、transportProperties文件
修改材料运动粘度为0.003333 m2/s,文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object transportProperties;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
transportModel Newtonian;
nu [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0] 0.003333;
2.4 设置边界条件与初始条件
1、p文件
p文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
object p;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 0;
boundaryField
{
INLET
{
type zeroGradient;
}
"(OUTLET1|OUTLET2)"
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 0;
}
WALLS
{
type zeroGradient;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
2、U文件
入口轴线上速度最大值为1 m/s,则该边界上平均速度为0.5m/s,这里采用codeFixedValue指定其充分发展速度条件。
算例中,。U文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volVectorField;
object U;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 1 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform (0.5 0 0);
boundaryField
{
INLET
{
type codedFixedValue;
value uniform (0 0.5 0);
name parabolicVelocity;
code
#{
// 下面三行为标准写法,一般不用修改
const fvPatch& boundaryPatch = patch();
const vectorField& Cf = boundaryPatch.Cf();
vectorField& field = *this;
// U_0为2倍的平均速度;p_ctr为中心点偏移量;p_r为半径
scalar U_0 = 1, p_ctr = 0, p_r = 0.5;
forAll(Cf, faceI)
{
field[faceI] = vector(0,U_0*(1-(pow(Cf[faceI].x()-p_ctr,2))/(p_r*p_r)),0);
}
#};
}
"(OUTLET1|OUTLET2)"
{
type zeroGradient;
}
WALLS
{
type noSlip;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
2.5 求解控制
1、controlDict文件
修改controlDict文件,设置迭代步数为3000,文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object controlDict;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
application simpleFoam;
startFrom startTime;
startTime 0;
stopAt endTime;
endTime 3000; //指定迭代次数
deltaT 1;
writeControl timeStep;
writeInterval 100;
purgeWrite 3;
writeFormat ascii;
writePrecision 6;
writeCompression off;
timeFormat general;
timePrecision 6;
runTimeModifiable true;
2、fvSolution文件
文件内容修改为:
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object fvSolution;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
solvers
{
p
{
solver GAMG;
tolerance 1e-06;
relTol 0.1;
smoother GaussSeidel;
}
U
{
solver smoothSolver;
smoother symGaussSeidel;
tolerance 1e-05;
relTol 0.1;
}
}
SIMPLE
{
nNonOrthogonalCorrectors 0;
consistent yes;
// 指定残差标准为1e-6
residualControl
{
p 1e-6;
U 1e-6;
}
}
relaxationFactors
{
equations
{
U 0.9;
".*" 0.9;
}
}
2.6 求解计算
采用pyFoamPlotRunner进行计算。注意事先安装好PyFoam。
pyFoamPlotRunner.py --clear simpleFoam
计算在迭代995步后收敛到1e-6,计算残差曲线如下图所示。
3 结果分析
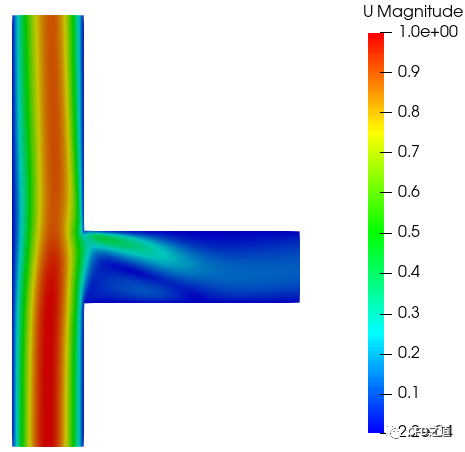
3.1 流场分布
-
速度分布
-
压力分布
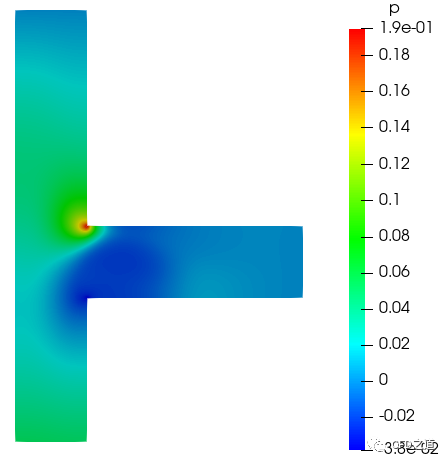
3.2 统计出口流量
出口流量的统计可以使用postProcess进行获取。
输入以下命令分别获取边界INLET、OUTLET1及OUTLET2的流量:
postProcess -latestTime -func "flowRatePatch(name=INLET)"
postProcess -latestTime -func "flowRatePatch(name=OUTLET1)"
postProcess -latestTime -func "flowRatePatch(name=OUTLET2)"
-
如下图所示,得到入口流量-0.0961673
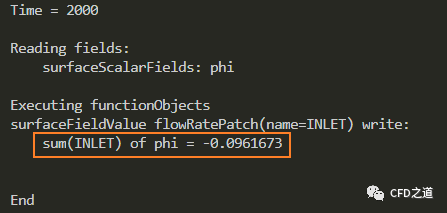
-
得到出口边界OUTLET1的流量为0.0111544
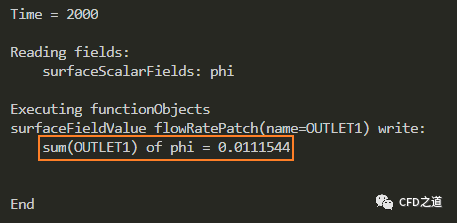
-
得到出口边界OUTLET2的流量为0.0850128
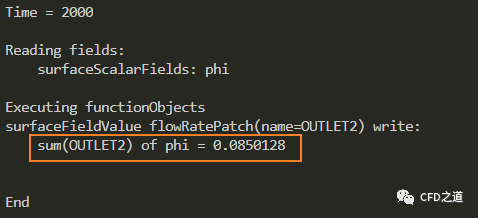
出口边界OUTLET2与入口的流量比为:
而文献给出的流量比为0.887,误差较小。
3.3 利用ParaView统计流量
除了可以利用postProcess提取进出口流量外,还可以在ParaView中获取进出口流量。
-
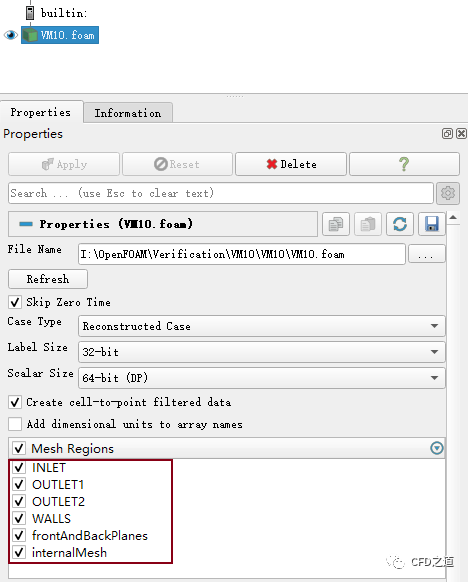
如下图所示,选择节点 VM10.foam,属性窗口中选中所有的边界
-
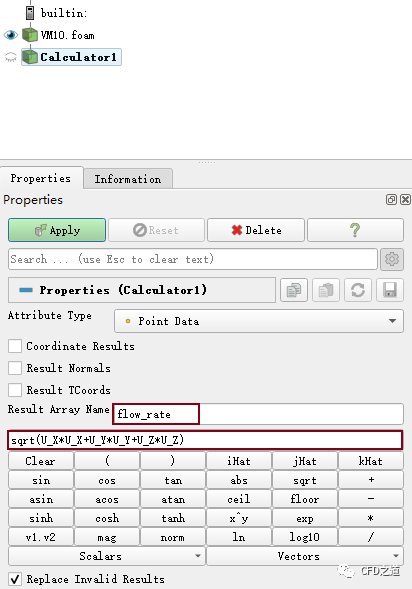
添加 Calculator,定义变量flow_rate,实际上定义的是合速度,合速度对面积求积分可得到体积流量
-
选中 Calculator1,选择菜单项Search...打开搜索对话框
-
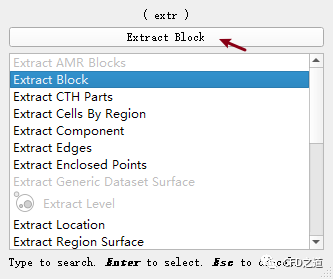
输入 Extract Block,如下图所示,选择使用按钮Extract Block
-
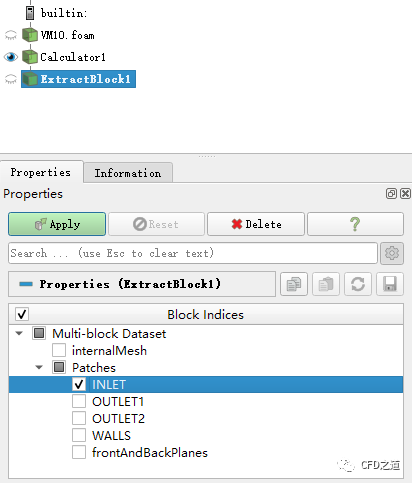
如下图所示选择 INLET边界面
-
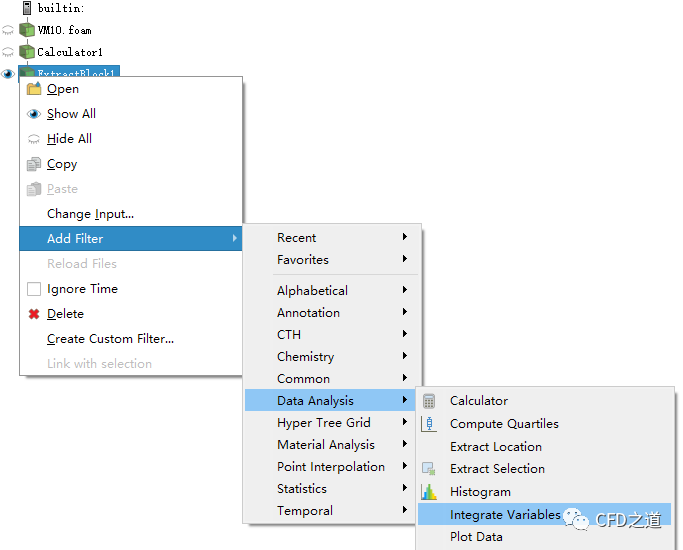
添加 Integrate Variables
-
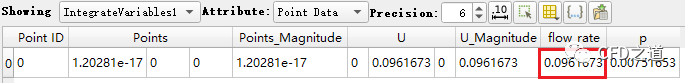
如下图所示,可以看到入口体积流量为 0.0961673
-
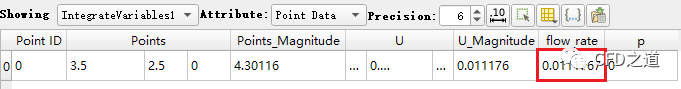
相同方式查看 OUTLET1边界的体积流量为0.0111767
-
相同方式查看
OUTLET2边界的体积流量为0.08501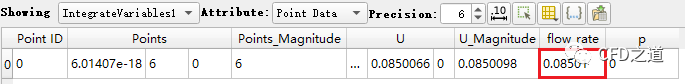
可以看到ParaView中统计得到的结果与前面postProcess得到的结果完全相符。
相关文件:

本篇文章来源于微信公众号: CFD之道








评论前必须登录!
注册